
Spinal Stenosis Surgery
10 Common Stenosis Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
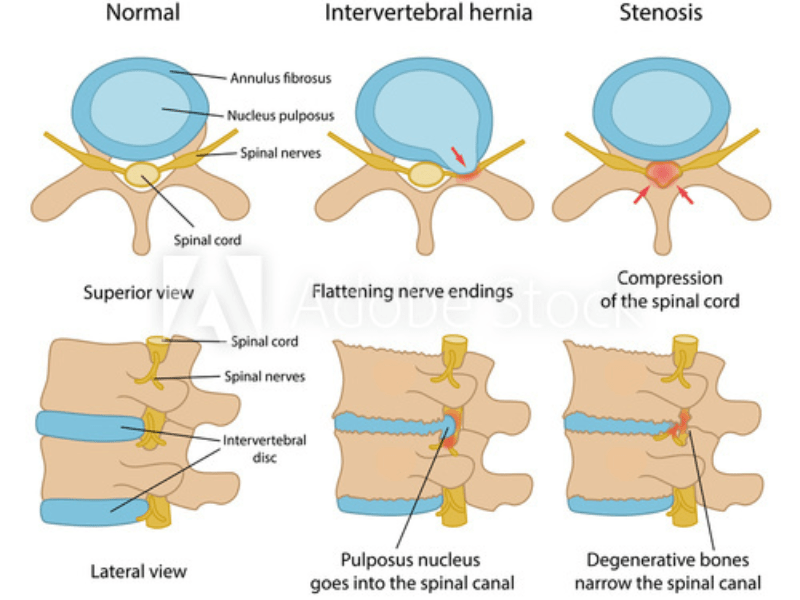
Stenosis is a medical condition that occurs when the spaces within the spine narrow, putting pressure on the nerves and causing pain and discomfort. If you experience any of the common symptoms of stenosis, it’s important to seek medical attention to prevent further complications. Learn about the warning signs here.
Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs.
One of the most common symptoms of stenosis is numbness or tingling in the arms or legs. This occurs when the nerves in the spine are compressed, causing a loss of sensation in the affected areas. If you experience numbness or tingling that persists or worsens over time, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Weakness in the arms or legs.
Another common symptom of stenosis is weakness in the arms or legs. This can occur when the nerves that control muscle movement are compressed in the spine. Weakness may be mild or severe and can affect one or both sides of the body. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience weakness, as it can impact your ability to perform daily activities and may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Pain in the neck or back.
Pain in the neck or back is one of the most common symptoms of stenosis. This pain can be dull or sharp and may radiate to other areas of the body, such as the arms or legs. The pain may be worse when standing or walking and may improve when sitting or lying down. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent pain, as it can impact your quality of life and may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Difficulty walking or standing for long periods of time.
Another common symptom of stenosis is difficulty walking or standing for long periods of time. This is because the narrowing of the spinal canal can put pressure on the nerves that control movement in the legs. You may experience weakness, numbness, or tingling in the legs, making it difficult to walk or stand for extended periods. If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Loss of bladder or bowel control.
Loss of bladder or bowel control is a serious symptom of stenosis that should not be ignored. This occurs when the narrowing of the spinal canal puts pressure on the nerves that control bladder and bowel function. You may experience difficulty urinating or having a bowel movement, or you may experience incontinence. If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately as this could be a sign of a more serious condition.
Causes of Spinal Stenosis?
Spinal stenosis is usually caused by general wear and tear that occurs during a lifetime. As a person ages, the discs located between each bone in the spine start to shrink, and the bones and ligaments start to thicken due to arthritis and chronic swelling. Spinal stenosis can also occur due to previous injuries, inherited conditions, trauma, or tumors of the spine.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Patients with lumbar spinal stenosis present with cramping or pain in the back, buttocks, thighs, or calves with decreased walking tolerance and weakness. In the lumbar spine, symptoms often increase when walking short distances and decrease when the patient sits, bends forward or lies down.
Symptoms of Cervical Spinal Stenosis
Patients with cervical spinal stenosis usually have numbness in the neck, shoulders, or arms that leads to cervical myelopathy. Severe cases of stenosis can also cause bladder and bowel problems.
Non-surgical Treatment of Spinal Stenosis
- Medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling and pain, and pain killers to relieve pain.
- Epidural steroid injections can help reduce swelling and treat acute pain that radiates to the hips or down the leg. This pain relief may be temporary.
- Rest or restricted activity
- Physical therapy and/or prescribed exercises to help stabilize the spine, build endurance and increase flexibility.
Surgical Treatment of Spinal Stenosis
Severe cases of stenosis often require surgery. The goal of the spinal stenosis surgery is to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or spinal nerve by widening the spinal canal.
- Decompressive laminectomy in which the roof of the vertebrae is removed to create more space for the nerves.
- Laminotomy: When only a small portion of the lamina is removed to relieve pressure on the nerve roots
- Foraminotomy: When the area where the nerve roots exit the spinal canal is removed to increase space over a nerve canal.
- Medial Facetectomy: When part of the bony structure in the spinal canal is removed to increase the space
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion : The cervical spine is reached through a small incision in the front of the neck. The intervertebral disc is removed and replaced with a small plug of bone, which in time will fuse the vertebrae.
- Cervical Corpectomy: When a portion of thevertebra and adjacent intervertebral discs are removed for decompression of the cervical spinal cord and spinal nerves. A bone graft, and in some cases a metal plate and screws, is used to stabilize the spine.
- Laminoplasty: A posterior approach in which the cervical spine is reached from the back of the neck and involves the surgical reconstruction of the posterior elements of the cervical spine to make more room for the spinal canal.
If nerves were badly damaged before the surgery, the patient may still have some pain or numbness after the surgery, or there may be no improvement at all. Also, the degenerative process of spine will continue, and pain or limitation of activity may reappear a few years after surgery. Most doctors will not consider surgical treatment of spinal stenosis unless several months of non-surgical treatment methods have been tried. Since all surgical procedures carry a certain amount of risk, patients are advised to discuss all treatment options with their doctor before deciding which procedure is best.
